1. Single-Tier Architecture
Introduction
A single-tier architecture refers to a basic application design where all components (such as the web server, application logic, and database) are hosted on a single instance or layer. This architecture is designed to be cost-effective, scalable, secure, and highly available.
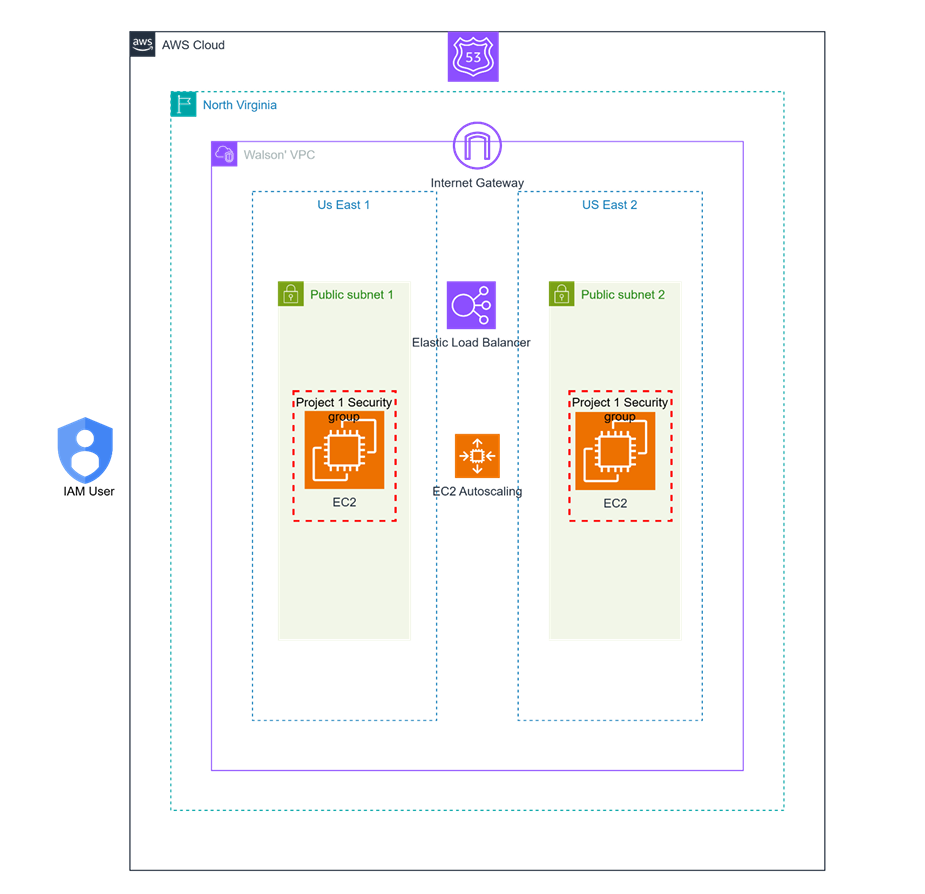
Architecture Overview
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): A logically isolated section of the AWS Cloud used to launch and manage AWS resources with custom IP ranges, route tables, and subnets.
- Subnets: Two public subnets hosting EC2 instances with internet access, helping organize resources and control traffic.
- Route 53: DNS service translating domain names into IP addresses to route user traffic to the application.
- Internet Gateway: Enables connectivity between the VPC and the public internet.
- Elastic Load Balancer: Distributes incoming traffic across EC2 instances to ensure availability.
- Security Group: Stateful firewall controlling inbound and outbound traffic to EC2 instances.
- EC2 Instances: Virtual servers hosting the web server, application logic, and database.
- EC2 Auto Scaling: Automatically adjusts the number of EC2 instances based on traffic demand for resource efficiency.
- IAM User: Controls access and permissions. Root user manages the account, and IAM roles grant temporary resource access securely.
Component Breakdown
| Service | How it Works |
|---|---|
| Route 53 | Translates domain names and directs incoming traffic to the ELB. |
| Elastic Load Balancer | Distributes incoming requests across healthy EC2 instances. |
| Security Group | Defines traffic rules that allow or deny access to EC2 instances. |
| Amazon EC2 | Hosts the application and handles traffic. |
| EC2 Auto Scaling | Scales the number of instances up or down based on traffic load. |
| S3 Bucket | Stores static content to offload requests from EC2 servers. |
| Internet Gateway | Facilitates communication between the VPC and the internet. |